
essential human anatomy and physiology pdf
Human anatomy and physiology explore the structure and functions of the body, essential for understanding health and disease. Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology provide comprehensive insights, blending clear explanations with detailed illustrations to facilitate learning.
Definition and Scope
Human anatomy focuses on the study of the body’s structure, including its organs, tissues, and cells, while physiology examines their functions and processes. Together, they provide a comprehensive understanding of how the body operates. The scope of anatomy and physiology spans from microscopic cellular activities to the integration of whole-body systems, offering insights into health, disease, and normal bodily functions. Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology cover these principles, making them foundational for medical education and scientific research.
Importance in Medical Education
Understanding human anatomy and physiology is fundamental in medical education, as it provides the foundation for diagnosing and treating diseases. These sciences explain how body systems interact, enabling healthcare professionals to comprehend pathological conditions. Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology are vital resources, offering detailed insights into the structure and function of the body. This knowledge is crucial for clinical practice, ensuring future healthcare providers can apply theoretical concepts to real-world patient care effectively.

The Importance of Textbooks in Studying Anatomy and Physiology
Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology are indispensable for structured learning, offering clear explanations and detailed visuals that simplify complex concepts for students.
Popular Textbooks and Their Features
Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology are widely recognized for their comprehensive content. The 10th and 12th editions, authored by Elaine N. Marieb and others, are popular choices. These textbooks feature detailed illustrations, clear explanations, and structured chapters that simplify complex anatomical and physiological concepts. They also include study tools like summaries, review questions, and visual aids to enhance learning. Their availability in PDF formats makes them accessible for digital learners. These resources are invaluable for students seeking a deep understanding of human anatomy and physiology.
How to Choose the Right Textbook
Selecting the right anatomy and physiology textbook involves considering factors like clarity, content depth, and visual aids. Look for editions that align with your course requirements, such as the 10th or 12th editions of Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology. Ensure the textbook includes features like detailed illustrations, review questions, and summaries. Digital formats, such as PDFs, offer flexibility and accessibility. Reading reviews and comparing content can help you choose a textbook that meets your learning needs and enhances your understanding of the subject.
Understanding the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood, functioning to transport oxygen and nutrients. Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology detail blood composition and circulation processes.
Structure and Function of the Heart
The heart is a muscular, hollow organ with four chambers: the right and left atria, and the right and left ventricles. It pumps blood through the cardiovascular system. Valves ensure blood flows in one direction, preventing backflow. The septum separates the atria and ventricles, maintaining proper blood circulation.
The heart’s electrical conduction system regulates contractions, enabling efficient pumping. Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology detail these structures and their roles in maintaining life-sustaining blood circulation.
Blood Composition and Circulation
Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. Plasma transports nutrients, hormones, and waste products, while RBCs carry oxygen. WBCs fight infections, and platelets aid in clotting. Circulation involves the movement of blood through arteries and veins, maintaining oxygen delivery and nutrient exchange. The cardiovascular system ensures blood reaches all tissues, sustaining life; Textbooks like Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology detail blood’s role in maintaining homeostasis and overall health.
Exploring the Respiratory System
The respiratory system includes the lungs, trachea, and bronchi, facilitating gas exchange. Air enters through the nose, passes the trachea, and reaches alveoli for oxygen diffusion.
Structure and Function of the Lungs
The lungs are vital organs located in the thoracic cavity, divided into lobes. Their elastic tissue allows expansion during inhalation. The alveoli, tiny air sacs, facilitate gas exchange, enabling oxygen to diffuse into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled. The lungs are protected by the ribcage and function in coordination with the diaphragm. Their structure ensures efficient respiration, maintaining oxygenation of the blood and overall bodily functions.
Gas Exchange and Breathing Mechanisms
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed. Breathing involves the contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, creating pressure changes to draw air into and out of the lungs. This process is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, ensuring continuous oxygen supply and carbon dioxide removal, vital for cellular respiration and maintaining acid-base balance in the body.
The Nervous System: Control and Coordination
The nervous system integrates and processes information to regulate body functions, enabling control and coordination of voluntary and involuntary actions through complex neural pathways.
Structure and Function of Neurons
Neurons, or nerve cells, are specialized cells designed for communication. Their structure includes dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. Dendrites receive signals, while the axon transmits them. The cell body contains the nucleus and organelles essential for cell function. Action potentials enable neurons to transmit electrical and chemical signals. Neurotransmitters are released at synapses, facilitating communication between neurons. This complex structure allows neurons to integrate and process information, enabling control and coordination of bodily functions. Understanding neuron structure and function is crucial for studying the nervous system’s role in human anatomy and physiology.
Reflexes and Sensory-Motor Integration
Reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli, involving neural pathways that connect sensory receptors to effector muscles. These pathways often pass through the spinal cord or brain. Sensory-motor integration refers to the nervous system’s ability to process sensory input and produce coordinated motor responses. Reflexes, such as withdrawing a hand from a hot surface, occur without conscious thought. This integration is vital for maintaining posture, balance, and reacting to environmental changes. Understanding reflex mechanisms provides insight into how the nervous system coordinates body functions efficiently.

Digestive System: Nutrition and Absorption
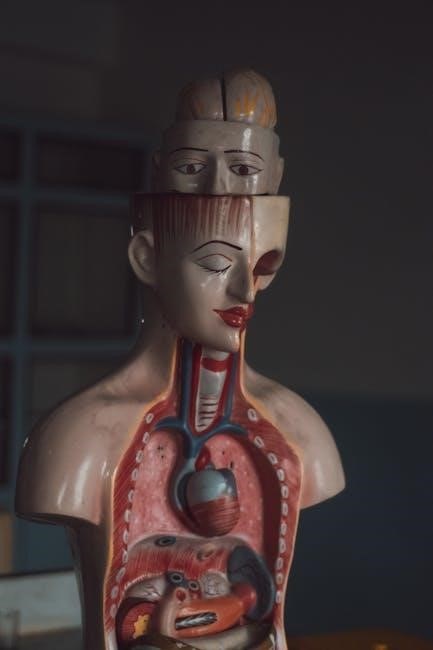

The digestive system processes food, enabling nutrient absorption for energy. The gastrointestinal tract, aided by enzymes, breaks down food into carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, facilitating absorption and waste elimination.
Structure and Function of the Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a tube-like structure extending from the mouth to the anus, consisting of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Its wall contains four layers: mucosa (innermost), submucosa, muscularis (muscle layer), and serosa (outermost). The GI tract performs ingestion, mechanical digestion (chewing, churning), chemical digestion via enzymes, absorption of nutrients in the small intestine, and water absorption and waste elimination in the large intestine. Enzymes like amylase, lipase, and trypsin break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into simpler molecules for absorption. This system ensures proper nutrient utilization and waste removal, maintaining homeostasis.
Role of Enzymes in Digestion
Enzymes play a crucial role in digestion by breaking down complex food molecules into simpler substances. Amylase in saliva and pancreatic juice breaks down carbohydrates into sugars. Lipase in the stomach and small intestine emulsifies fats into fatty acids and glycerol. Proteases like pepsin and trypsin break proteins into amino acids. These enzymes ensure efficient nutrient absorption, maintaining proper bodily functions. Without enzymes, digestion would be inefficient, leading to malnutrition and health issues, emphasizing their vital role in the digestive process.
Musculoskeletal System: Movement and Support
The musculoskeletal system, comprising bones, joints, and muscles, enables movement, provides structural support, and protects internal organs. It is essential for locomotion and maintaining posture.
Structure and Function of Bones and Joints
Bones provide structural support, protect internal organs, and facilitate movement. They are classified into long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid bones, each serving specific functions. Joints, where bones meet, allow for flexibility and movement. There are three types: synovial, cartilaginous, and fibrous joints. Synovial joints, like the knee, offer the widest range of motion. Bones and joints work together to enable locomotion, maintain posture, and support bodily functions. Their integrity is vital for overall musculoskeletal health and mobility.
Muscle Types and Their Functions
Muscles are classified into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles, attached to bones, enable voluntary movements and maintain posture. Smooth muscles, found in internal organs, perform involuntary actions like digestion. Cardiac muscles, exclusive to the heart, ensure continuous pumping of blood. Each type has unique structural and functional adaptations, such as striations in skeletal and cardiac muscles for precise control. Together, they facilitate movement, regulate bodily processes, and maintain overall physiological balance, essential for survival and daily activities.
Related Posts

acls exam version c answers pdf
Get ACLS Exam Version C answers in PDF format. Free study guide, practice questions, and instant download. Prepare smarter, not harder!

explaining adhd to a child pdf
Learn how to explain ADHD to children in a simple, engaging way. Download our free PDF guide to help kids understand and manage their ADHD.

john paul jackson books pdf free download
Access John Paul Jackson’s books for free in PDF. Instantly download his spiritual teachings and revelations.